Rancher Desktop
Mac, Windows, and Linux
As of January 2022 with the release of version v1.0 you can install Rancher Desktop on Windows, Mac and Linux. Rancher Desktop runs up a VM on all three, which allows Rancher Desktop’s kubernetes install to be isolated from your desktop.
I have installed v1.0.1 onto a Mac, by downloading the .dmg from https://github.com/rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop/releases (plus-open the Assets and download Rancher.Desktop-1.0.1.x86_64.dmg).
I have also installed on GNU Linux Ubuntu 20.04 desktop, by adding their repo - but you could download the .deb - details here https://software.opensuse.org/download.html?project=isv%3ARancher%3Astable&package=rancher-desktop.
Running
Run the Rancher Desktop application from the “Start” or “Applications” menus / Dock, and you will see the Rancher Desktop application and a friendly horned computer logo in the notification area ![]() .
.
You can select how much RAM and how many CPU cores to assign to the virtual machine, and you can pick which version of Kubernetes to install.
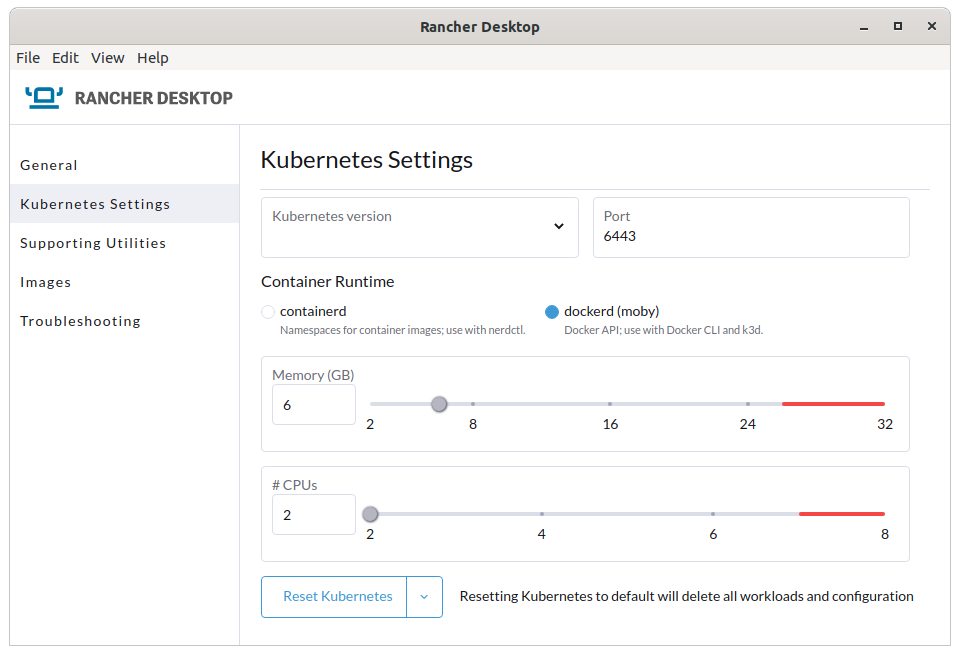
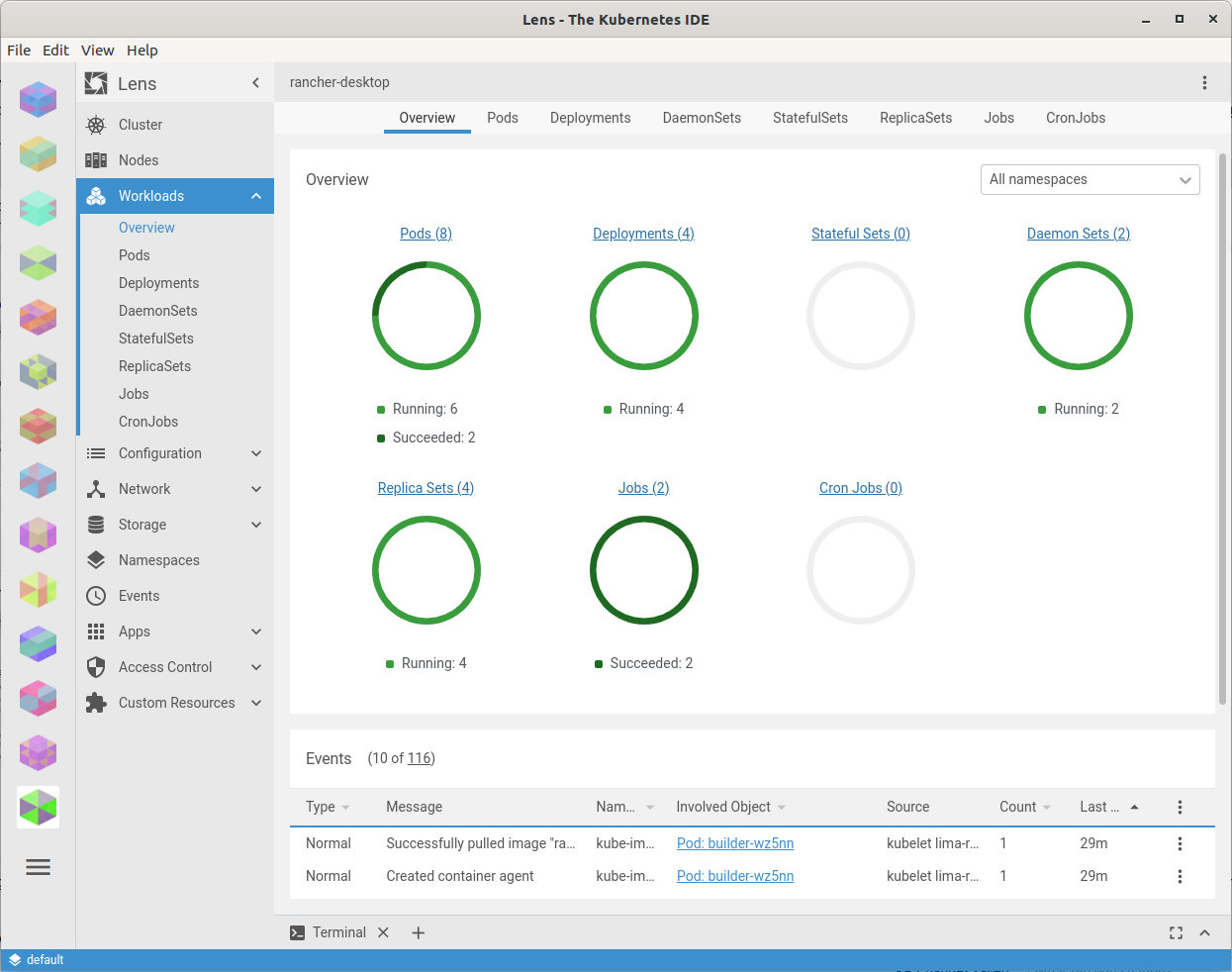
At this point you have a single node kubernetes cluster called rancher-desktop running on your local machine. You can interact with it with the standard kubernetes tools, including kubectl, helm - which Rancher Desktop kindly installed for you:
$ kubectl get nodes --context rancher-desktop
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
lima-rancher-desktop Ready builder,control-plane,master 35m v1.21.5+k3s2
… and also other tools like Lens https://k8slens.dev/.
Work in Progress
Rancher Desktop is a work in progress - there are a few rough edges and the documentation is a little lacking, but there are some fun workarounds and an active Slack channel.
The User Interface is missing the ability to set some important settings in the container runtime, which are expected to de developed over the next few months.
But I believe Rancher Desktop is already capable of replacing Docker Desktop - if you poke it with some workarounds.
Containerd or Dockerd (moby)
Rancher Desktop was originally developed to use containerd as its container runtime. The documentation of workarounds is mostly for containerd. But there are issues when building container images using containerd and it’s command line tool nerdctl.
You are supposed to be able to substitute nerdctl for docker (or create an alias) - the CLI commands are supposed to be identical, but there are a few issues. The most notable issues using nerdctl are building images FROM local images and copying using COPY --from a local image. These commands do not work. https://github.com/containerd/nerdctl/issues/434
Because of that issue, Rancher Desktop can now be switched to use dockerd as the container runtime (okay - it’s actually containerd underneath dockerd, but dockerd is in control). This means you can use the docker command line tool (which also comes bundled with Rancher Desktop) and building images works as expected.
Get a shell into the Rancher Desktop VM
Since Rancher Desktop spins up a VM in which it runs containerd or dockerd, using Qemu or a WSL instance on Windows, there might be occasions when it would be useful to access the VM - for investigating issues, for instance.
On a Mac you do this - it’s all one command and the quotes around the paths is important due to there being spaces in them:
LIMA_HOME="$HOME/Library/Application Support/rancher-desktop/lima" \
"/Applications/Rancher Desktop.app/Contents/Resources/resources/darwin/lima/bin/limactl" \
shell 0
On Linux you do this - it’s all one command:
LIMA_HOME="$HOME/.local/share/rancher-desktop/lima" \
/opt/rancher-desktop/resources/resources/linux/lima/bin/limactl \
shell 0
Problems
Configuring the Rancher Desktop container runtime to pull images from private repositories is difficult
I am sure you are all aware of the need to edit dockerd’s daemon.json file to include insecure-registries and registry-mirrors. In Docker Desktop you can edit that in the GUI (here’s an image from the Internet).

In Rancher Desktop’s GUI you cannot currently edit that file (or the similar file that has edited when you are using containerd as the container runtime). But there is a workaround.
Inside a VM
Since Rancher Desktop (and Docker Desktop) both run the container runtime inside a VM, all configuration for the container runtime is inside a VM. It’s hard to edit files in the VM, which is why Docker Desktop includes that ability in its GUI.
The configuration file for dockerd is /etc/docker/daemon.json inside the VM. The configuration file for setting containerd’s registries in Rancher Desktop is /etc/rancher/k3s/registries.yaml inside the VM.
It is possible to inject commands into the boot-up sequence of the Rancher Desktop VM, so we can make the configuration file for dockerd and containerd at VM start, and the container runtime will pickup the settings when it starts inside the VM.
Workaround
You can define both /etc/rancher/k3s/registries.yaml and /etc/docker/daemon.json in one go by creating override.yaml in the following location:
- Linux:
$HOME/.local/share/rancher-desktop/lima/_config/override.yaml - Mac:
$HOME/Library/Application Support/rancher-desktop/lima/_config/override.yaml
Here’s an example override.yaml
provision:
- mode: system
script: |
#!/bin/sh
set -eux
mkdir -p /etc/rancher/k3s
cat <<EOF >/etc/rancher/k3s/registries.yaml
mirrors:
docker.io:
endpoint:
- "http://nexus.lan:8084"
nexus.lan:
endpoint:
- "http://nexus.lan:8084"
EOF
mkdir -p /etc/docker
cat <<EOF >/etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"insecure-registries" : ["nexus.lan:8084"],
"registry-mirrors": ["http://nexus.lan:8084"],
"experimental": true
}
EOF
On Windows I think you just edit /etc/docker/daemon.json in the WSL image and restart Rancher Desktop.
See https://github.com/rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop/issues/721.
Nerdctl cannot build images FROM local images or using –copy-from from local images
See https://github.com/containerd/nerdctl/issues/434.
Workaround
Switch the container runtime from containerd to dockerd (moby).
Rancher Desktop binds to ports 80 and 443
When Rancher Desktop is started it binds to ports 80 and 443, which may conflict with other software you may be running. This is because Rancher Desktop runs k3s as the Kubernetes implementation, and by default it runs Træfik as the ingress controller.
Workaround
Uninstall Træfik:
helm uninstall traefik --namespace kube-system
helm uninstall traefik-crd --namespace kube-system
kubectl delete helmcharts traefik --namespace kube-system
kubectl delete helmcharts traefik-crd --namespace kube-system